Osteoarthritis
What is Osteoarthritis?
Osteorthritis is the most common type of arthritis in the UK. It develops over time especially after the age of 50.
It is often referred to as 'wear and tear' of the joints and can be a result gradual degeneration and accumulation of repeated minor damage over the years. Sometimes it is caused by a previous significant injury like a fracture or dislocation. In some cases, there is a strong family history while sometimes it is resultant of many years of suffering with gout.
Most commonly affected joints are hips and knees, but hands,spine and ankles and feet are also affected.
For more information on the condition, please look on this NHS website.

What are the key aspects of living and managing osteoarthritis?
Below are some of the key aspects of managing and preventing the progression of osteoarthritis:
- ensuring regular exercise
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Appropriate footwear
- Pain management
- Splints and walking aids
- Surgical options.
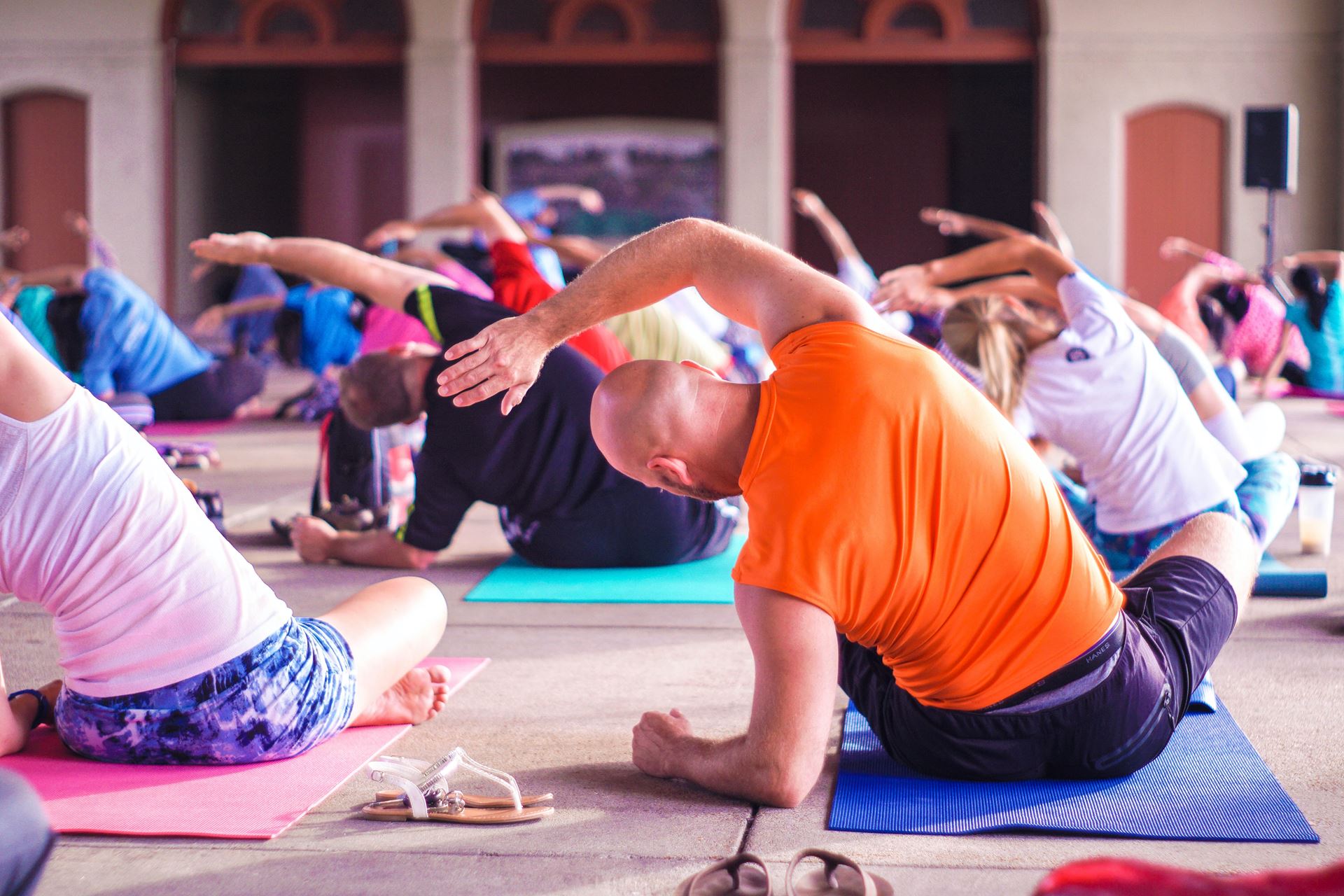
Benefits of Exercise.
Exercise has many well known benefits to your mental and physical wellbeing . It is also a great way to help prevent pain, reduce your weight, help maintain balance and improve posture.
Exercises comes in many forms and have different benefits to help manage your condition. Just doing a 2-3 hours of gentle to moderate exercise a week has been shown to have th emost benefit
1: Strengthening exercises can greatly help with stability of the joint and help to reduce pain. Exercises like Pilates and Tai Chi are great examples of this and easy to do at all levels.
2:Aerobic exercise like swimming, walking running cycling or certain exercise classes improves your cardio health, mental health and stamina.
3: Balance exercises can help improving with stability of your joints and can help greatly with preventing falling.
4: Stretching exercises can help reduce stiffness increase flexibility and maintain balance.
Click here for more information about the above exercises
Our community NHS physiotherapy team can give you specialist advice on the above. See the link above.

Weight Loss Support
It can be a difficult task trying to lose weight and keeping it off, especially when you are already feeling stiff and in pain. In our experience, the most succesful regimes recommend a small but consistent shift in lifestyle and diet over a long period time.
If you are overweight or obese and struggling to lose the weight on your own, please look at the weight loss support link below. Within the link, you can also fill in the form for a referral to our NHS dieticians. They run an excellent weight reduction programme, the team have considerable experience and can give professional and specialist dietetic advice on how to lose weight effectively.
The vicious cycle of weight gain, lack of exercise and osteoarthritis
It can be a difficult task trying to lose weight and keeping it off, especially when you are already feeling significant stiffness and pain.
The most succesful regimes, in our experience, recommend a small but consistent shift in lifestyle and diet over a long period time. If you are overweight or obese and struggling to lose the weight on your own please look at the weight loss support link above. There is also a link for a referral to our NHS dieticians. They run an excellent weight reduction programme. The team have considerable experience and can give professional and specialist dietetic advice on how to lose weight effectively and successfully.
Importance of healthy weight
We are all different shapes and sizes which can make it difficult to know what a healthy weight actuallyis. Working out your BMI (body mass index) is a useful marker for understanding what your optimal weight should be.
- A healthy BMI is somewhere between 18-25
- Overwieght is above 25
- Obese is above 30
Being overweight or obese will over time have a significant impact on the progression of you arthritis particulalry the hip, knees and ankles.
The role of footwear and arthritis
It is important to be aware about footwear and the impact it has on helping and maintaining balance, joint stability and preventing falls.
Orthotics support: simple insole supports to your shoes can be bought in supermarkets, online and in your local pharmacy . These can have a major benefits in supporting the sole of your foot if you have overly flat or high arches. Look at the heel of your usual shoes to see if there is assymetrical wearing to give you an idea of the issue. Individuals with flat feet usually wear our the inner aspect of shoe heel, while people with high arches tend to over pronate the foot and wear out the heel on the outer aspect of the shoe.

Podiatry advice
Podiatrists also known as chiropodists are qualified foot experts who can give specialist advice on
- insoles, splints and supports
- footwear
- exercise
- medication.
A podiatrist can treat problems caused by the way the foot and ankle work, which commonly affect your hip and knees.
They can recommend specialist orthotic advice on splints or insoles. Tailored designed to support and correct the position of your foot or ankle, reducing the risk of further damage to your joints.
You can self refer to an NHS podiatrist by clicking on the link below.
Treatments
Osteoartritis is one of the most common causes for seeing the clinical team in general practice.
Our Key areas of focus for treatment centre on:
- Pain medication
- Splints
- Alternative therapies
- Surgical options
Pain Medication
Pain relief medication is just one part of the range of treatments available for treating chronic pain associated with arthritis.
- Oral Medication : Paracetamol and Non-Steroidal Anti-inflammatory (NSAIDs) medication (ibuprofen, naproxen etc)
- Topical Therapy: voltarol gel/ ibugel localised to the affected joint is a useful especially if you are at risk of side effects of oral NSAIDS
- Opiate based medication - (codeine, co-codamol, morphine) very useful for severe attacks of pain but would strongly advise against frequent and regular use.
- Neuromodulator medication: like antidepressants, Gabapentin/pregabalin medication can help reduce the severity and reduce the suffering associated with chronic pain
Please see our chronic pain page for more advice on chronic page management. (see link below)
Alternative Therapies
There are multiple therapies for arthritis include:
1:Manual massage therapy often recommended and sometimes undertaken by specialist massage therapists or physiotherapists.
2: Hydrotherapy/ aquatic therapy can be recommended by sports trainers and physiotherapists alike. click here for more info.
3: Heat Therapy: localised cold/ice packs, deep heat cream, localised heat therapy. Cold water therapy like outdoor swimming has been helpful
4: Knee or shoulder steroid injections given by our GP's Click here for more information
5: TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation) machines for more information click here
Splints, Straps and Walking aids
Splints are often used for hands and wrists while braces and straps are geared for more knee, ankle and elbow issues. These devices are generally designed to provide protection and support to the weak ,swollen, painful and stiff joints.
Wrist and hand splints can be divided into resting and working splints. For more information on the differences and benefits of each type of splint click here.
These supportive devices can be purchased privately online or in pharmacies. Physiotherapist might be able to provide more tailored advice about the right supportive device if you are unsure about which one to use, including how and when to use it . See the link above for physiotherapy self-referral.
Walking aids can be very helpful to support mobility and day to day functioning . They can range from a simple walking stick to zimmer frame or delta walker. An occupational therapist (OT) or physiotherapist can offer further advice on which would be most suitable. Please click on the link below for self referral form to arrange an appointment for walking aid assessment.
Page created: 04 September 2020