Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
What is PCOS?
PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome) is a common condition that affects how a woman's ovaries work. The 3 main features of PCOS are:
- irregular periods – which means your ovaries do not regularly release eggs (ovulation)
- excess androgen – high levels of "male" hormones in your body, which may cause physical signs such as excess facial or body hair
- polycystic ovaries – your ovaries become enlarged and contain many fluid-filled sacs (follicles) that surround the eggs (but despite the name, you do not actually have cysts if you have PCOS)
Symptoms of Polycystic Ovaries
If you have signs and symptoms of PCOS they'll usually become apparent during your late teens or early 20s.
They can include:
- irregular periods or no periods at all
- difficulty getting pregnant as a result of irregular ovulation or no ovulation
- excessive hair growth – usually on the face, chest, back or buttocks
- weight gain
- thinning hair and hair loss
- oily skin or acne
PCOS is also associated with an increased risk of developing health problems in later life, such as type 2 diabetes and high cholesterol levels.

Causes and Treatment
What Causes PCOS?
The exact cause of PCOS is unknown, but it often runs in families.
It's related to abnormal hormone levels in the body, including high levels of insulin (Insulin is a hormone that controls sugar levels in the body)
Many women with PCOS are resistant to the action of insulin in their body and produce higher levels of insulin to overcome this, which contributes to the increased production and activity of hormones like testosterone.
Being overweight or obese also increases the amount of insulin your body produces. Visit our weight management page for more information.
Treatment
There's no cure for PCOS, but the symptoms can be treated. Speak to one of our clinicians if you think you may have PCOS.
If you're overweight, losing weight and eating a healthy, balanced diet can make some symptoms better.
Medicines are also available to treat symptoms such as excessive hair growth, irregular periods and fertility problems- if fertility medicines are not effective, a simple surgical procedure called laparoscopic ovarian drilling (LOD) may be recommended. This involves using heat or a laser to destroy the tissue in the ovaries that's producing androgens, such as testosterone.
With treatment, most women with PCOS are able to get pregnant.
PCOS and The Pill
The contraceptive pill may be recommended to induce regular periods, or periods may be induced using an intermittent course of progestogen tablets (which are usually given every 3 to 4 months, but can be given monthly).
This will also reduce the long-term risk of developing endometrial cancer (cancer of the womb lining) associated with not having regular periods.
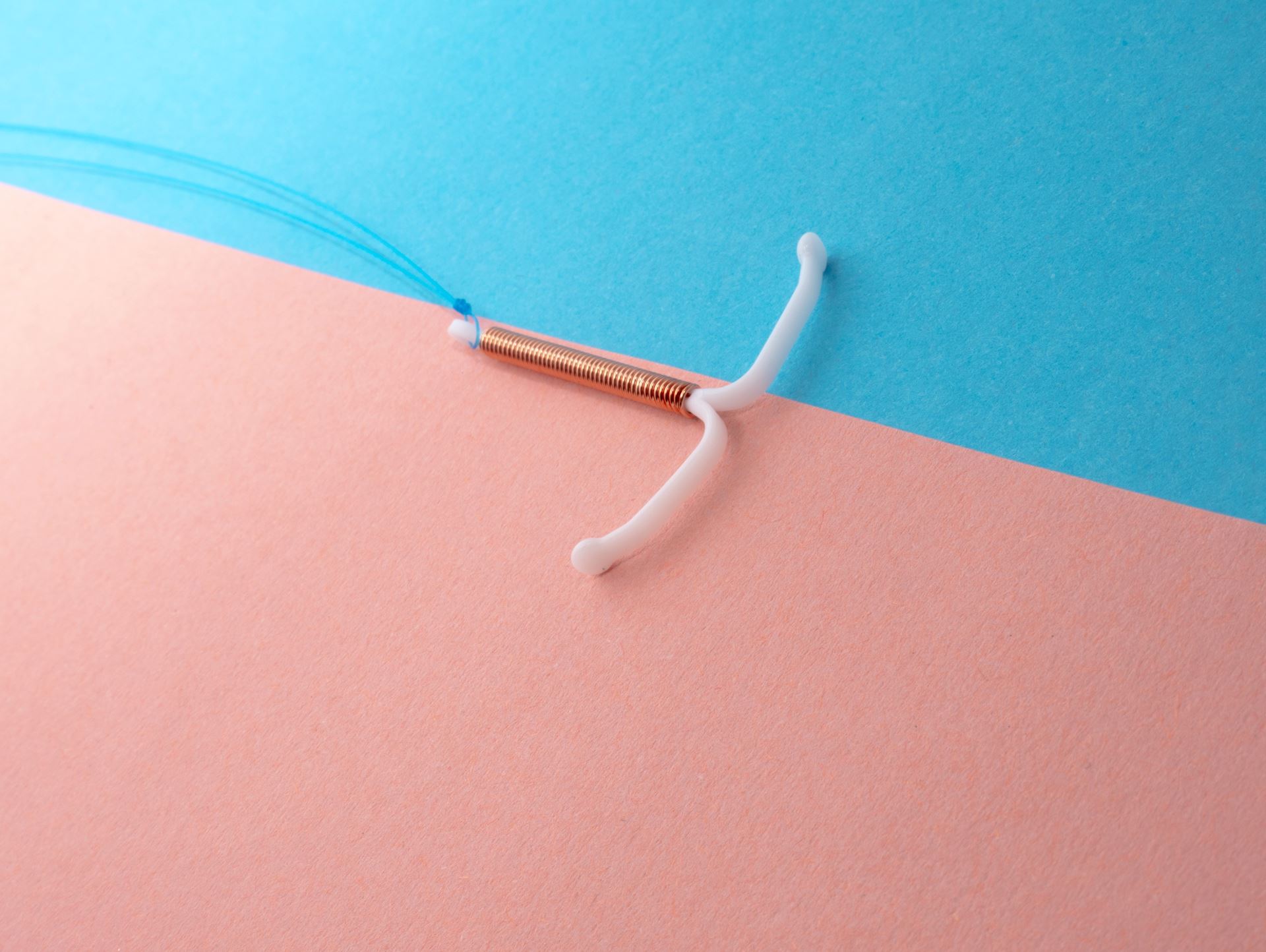
Other hormonal methods of contraception, such as an intrauterine system (coil), will also reduce this risk by keeping the womb lining thin, but they may not cause periods.
Please click the images opposite to visit the contraceptive pill and coil pages.
Page created: 04 September 2020